Ryobi is a popular brand that specializes in power tools, including drills. However, like any other tool, Ryobi drills can encounter various problems due to wear and tear or misuse.
These issues can affect the performance of your drill and make your work more challenging. In this guide, we will discuss eight common Ryobi drill problems and how to fix them.
First Thing First:
Before we dive into the specific problems and fixes, there are a few essential things to know about Ryobi drills. First and foremost, make sure to read the user manual thoroughly before using your drill.
The manual contains troubleshooting assistance that can help you identify and solve common issues with your Ryobi drill.
Additionally, if you encounter any problems with your Ryobi drill, remember that the company offers a refund or replacement within 90 days of purchase.
Furthermore, all Ryobi drills come with a warranty period of three years for residential use and one year for commercial use.
Lastly, keep in mind that the average lifespan of a Ryobi drill is between 8 to 14 months, depending on usage and maintenance. Therefore, it’s essential to take good care of your drill to ensure its longevity.
8 Ryobi Drill Problems And Solution:
1. Battery Not Charging:
If you notice that your Ryobi drill’s battery is not charging, the first thing to do is check the charger and make sure it is properly plugged in.
If the charger seems to be working correctly, there may be an issue with the battery itself.
To fix a Ryobi drill battery that is not charging, Firstly, you can try pulse charging the battery by plugging and unplugging the charger (with the battery in it) for 10 seconds at a time until the battery begins to charge.
This method is particularly useful if the battery has been left in the charger for too long, which can drain the battery and make it appear defective.
Secondly, you can try cleaning the battery contacts on both the tool and the battery to ensure that they are free from dirt or debris that may be preventing the battery from charging properly. This can be done using a dry cloth to gently clean the contacts.
Thirdly, you can try jump-starting the battery using another battery or a charger with a higher voltage. This method is particularly useful if the battery has been completely drained and the charger is unable to recognize it.
Fourthly, you can try storing the battery in a charged condition of a minimum of 2 bars of charge on the gauge to prevent it from losing its ability to hold a charge.
This can be done by charging the battery regularly and avoiding leaving it in the charger for extended periods of time.
Finally, if none of these solutions work, you may need to replace the battery or the charger, particularly if they are several years old and have been charged and discharged numerous times.
It is important to note that lithium-ion batteries, such as those used in Ryobi drills, can lose their ability to hold a charge over time, particularly if they are not stored properly or are subjected to extreme temperatures.
Therefore, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for storing and charging the battery to ensure that it lasts as long as possible.
2. Chuck Dysfunction
One common issue that users encounter with their Ryobi drills is dysfunction in the chuck mechanism.
The chuck, responsible for holding drill bits securely in place, can sometimes fail to operate as intended, leading to frustration and delays in work. There are several potential causes for this dysfunction.
Firstly, the chuck may become stuck or jammed due to over-tightening or the accumulation of debris. In such cases, gently tapping the chuck or cleaning it thoroughly can often resolve the issue.
Another possibility is that the chuck key, if applicable, is not engaging properly with the chuck teeth, hindering its ability to tighten or loosen effectively.
Additionally, wear and tear over time can lead to diminished grip strength, necessitating a replacement of the chuck.
If these troubleshooting steps fail to rectify the problem, it may indicate internal mechanism issues, warranting professional inspection or contacting Ryobi customer support for assistance.
3. Charging Hurdles
In addition to battery charging issues, Ryobi drills may also encounter problems with the charger itself.
One common problem is a loose or damaged power cord, which can cause intermittent charging or no charging at all. In such cases, replacing the cord or tightening any loose connections should solve the issue.
Another hurdle that users may face is a faulty internal component in the charger, such as a capacitor or transformer. In such cases, it is best to consult a professional for repair or consider purchasing a new charger.
4. Motor Malfunction
Motor malfunction is another common problem reported by users of Ryobi drills. This can manifest in various ways, including a burning smell, sparks from the motor, or failure to start.
One potential cause of motor malfunction is overheating, often due to prolonged use or lack of proper ventilation during use. In such cases, allowing the drill to cool down and using it in shorter bursts can help prevent further damage.
Another possible culprit is a worn out or damaged armature, which may require replacement by a professional. Additionally, issues with the gears or bearings can also lead to motor malfunction and may require expert troubleshooting.
5. Ryobi Drill Not Turning On
Even after following the charging issues, if your ryobi drill is not turning on, the issue might lie in trigger malfunctioning.
trigger is the button that starts the drill. In some cases, the trigger may become stuck or unresponsive due to debris buildup or wear and tear from frequent use.
To fix this issue, you can try cleaning the trigger with compressed air or a small brush to remove any dirt or debris that may be hindering its function.
If cleaning or replacing the trigger does not solve the issue, conducting an electrical test to check the trigger’s functionality might be necessary. For this, you will need a multimeter to measure the resistance between its contacts while pressing the trigger. Here’s how you can perform this test:
- Safety First: Ensure the drill is completely turned off and the battery is removed to avoid any accidental start-up or electrical shock.
- Access the Trigger Contacts: Disassemble the drill housing carefully to access the trigger mechanism. This process might vary depending on the specific Ryobi drill model, so refer to the user manual for detailed instructions.
- Set up Your Multimeter: Turn your multimeter to the resistance measurement setting (Ohms Ω). If your multimeter has multiple ranges, select a mid-range setting.
- Measure the Resistance: Place one multimeter probe on each contact of the trigger. Make sure the probes have a good connection to the metal contacts.
- Press the Trigger: While holding the probes in place, press the trigger. The resistance should change significantly from when the trigger is not being pressed to when it is. A functioning trigger will show low resistance (close to zero Ohms) when pressed, indicating a good electrical path.
If the multimeter does not show any change in resistance when the trigger is pressed, there may be an issue with the electrical path within the trigger mechanism.
This could be due to worn contacts, a broken wire, or another internal failure. In such cases, the trigger assembly may need to be replaced.
Conversely, if the resistance changes appropriately, the trigger mechanism is likely working correctly, and further troubleshooting may be required elsewhere in the drill’s electrical system.
6. Motor Spinning Slowly / Torque Dilemmas
Another common issue users may encounter with their Ryobi drill is the motor spinning much slower than usual or lacking sufficient torque.
This can be a frustrating problem that hinders the drill’s performance and efficiency. The most common cause of this issue is a worn out or faulty gear assembly.
To address this issue, disassemble the drill and inspect the gear assembly for any damage, wear, or debris. If necessary, replace any damaged gears and clean out any accumulated debris. It is essential to use the correct gear assembly for your specific drill model to ensure proper functioning.
In some cases, the motor itself may be the problem if it has sustained damage or worn out over time. In such cases, professional repair or replacement of the motor may be necessary.
7. Addressing Armature Issues
Another potential issue users may face with their Ryobi drill is interruptions during spinning, indicated by a jerking or halting motion. This can be caused by problems with the armature, which is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical power.
Armature comprises a series of copper wire windings that rotate along with the motor (As shown in image).

If these windings become damaged, corroded, or worn out, it can lead to interruptions in the spinning motion.
To address this issue, disassemble the drill and inspect the armature for any signs of damage or wear. If necessary, replace the armature with a new one from Ryobi or a third-party supplier. It is crucial to ensure that the replacement armature is compatible with your specific drill model to prevent any further issues.
7. Addressing Broken Magnets
In rare cases, the motor may fail entirely due to broken or missing magnets. These small magnets are responsible for creating the magnetic field that helps drive the rotation of the armature.
If these magnets become damaged or fall out, it can lead to complete motor failure. In such cases, professional repair or replacement of the motor may be necessary.
To prevent this issue, it is essential to handle your Ryobi drill with care and avoid dropping it or subjecting it to any severe impacts that can damage the motor’s internal components.
8. Addressing Carbon Brushes Wear and Tear
Carbon brushes are small conductive pieces that transfer electricity from the drill’s power source to the motor’s armature (As shown in image). These brushes can wear out over time due to frequent use, causing a decrease in performance or complete failure of the drill.
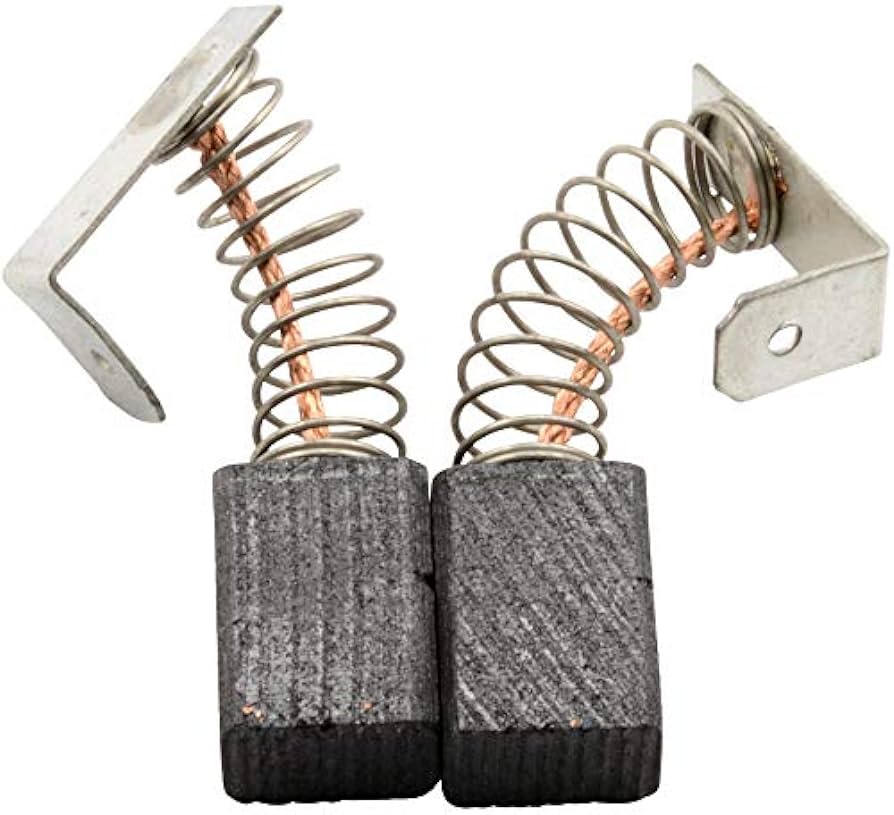

To address this issue, disassemble the drill and inspect the carbon brushes for any signs of damage or wear. If necessary, replace the carbon brushes with new ones from Ryobi or a third-party supplier. It is crucial to ensure that the replacement brushes are compatible with your specific drill model to prevent any further issues.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while Ryobi drills are known for their durability and reliability, like any other power tool, they may experience issues over time due to wear and tear or mishandling. However, most of these issues can be easily addressed with some basic maintenance and troubleshooting techniques.
It is essential to always refer to the user manual for detailed instructions on disassembling and reassembling your specific Ryobi drill model. Additionally, using genuine Ryobi replacement parts can ensure proper functioning and prevent further issues.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can troubleshoot and address common problems with your Ryobi drill and get it back to working efficiently in no time. Remember to always prioritize safety and exercise caution when handling power tools to avoid any accidents or injuries. Happy drilling!